Collection: Fuses & Varistors
In electricity, a fuse is a component consisting of a suitable support and a filament or sheet of a metal or alloy with a low melting point that is inserted at a specific point in an electrical installation so that it melts (by Joule effect) when the current intensity exceeds (due to a short circuit or excessive load) a certain value that could endanger the integrity of the installation's conductors with the consequent risk of fire or destruction of other elements.
On the other hand, a varistor is an electronic component with a characteristic curve similar to that of a diode. The term comes from the contraction of the English expression "variable resistor." Varistors are often used to protect circuits against voltage fluctuations by incorporating them into the circuit so that when activated, the current does not pass through sensitive components. A varistor is also known as a Voltage Dependent Resistor or VDR. The function of the varistor is to conduct a significant current when the voltage is excessive.
-
GC-0930 Automotive ATC Fuse Kit [10 PCS] - (AD57299)
Regular price $1.95 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
65900 Automotive Mini Fuse Kit [10 PCS] - (AD30287)
Regular price $2.61 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
ES1373A-KIT Automotive Micro Fuse Kit [10 PCS] - (AD30036)
Regular price $2.92 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
AC-1509 Earthenware Fuses Kit (90 PCS) - (AD61313)
Regular price $4.38 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
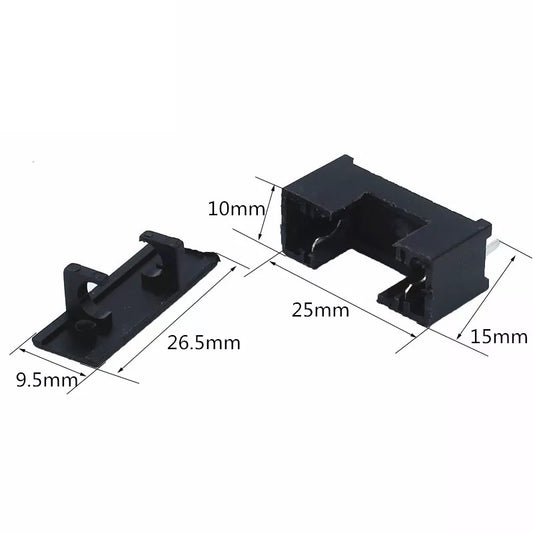
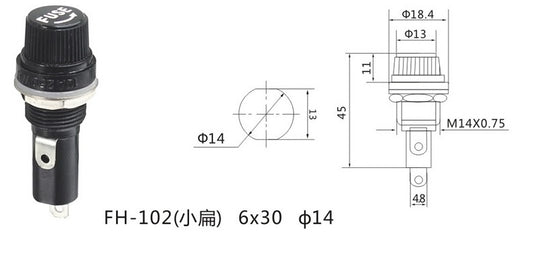
FS-1 6x32mm Panel Mount Fuse Holder - (AD2796)
Regular price $1.95 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
FS-2 5x20mm Panel Mount Fuse Holder - (AD2800)
Regular price $1.73 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
SIT-3308 Fuse Holder With Cover 5x20mm 250V @ 4A - (AD5714)
Regular price $0.84 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
BLX-A Fuse Holder With Cover 5x20mm 250V @ 6.3A - (AD14958)
Regular price $0.84 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
5x20mm In-Line Fuse Holder - (AD2874)
Regular price $0.88 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
6x32mm In-Line Fuse Holder - (AD2877)
Regular price $2.61 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
CQ-210-10 6x32mm In-Line Fuse Holder - (AD48903)
Regular price $4.07 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
CQ-211C-12 ATC Fuse Holder - (AD79745)
Regular price $3.98 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
12V Car Mini ATM - APM Blade Fuse Holder - (AD50854)
Regular price $2.61 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
12V Car Fuse Holder Kit (9 PCS) - (AD28842)
Regular price $5.75 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
T500mA Capacitive Cylindrical Fuse 250V @ 500mA - (AD73585)
Regular price $2.61 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
T1A Capacitive Cylindrical Fuse 250V @ 1A - (AD73616)
Regular price $2.61 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
T2.5A Capacitive Cylindrical Fuse 250V @ 2.5A - (AD35679)
Regular price $2.61 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
T3.15A Capacitive Cylindrical Fuse 250V @ 3.15A - (AD73584)
Regular price $2.61 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
T5A Capacitive Cylindrical Fuse 250V @ 5A - (AD73617)
Regular price $2.61 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
FM-0.1A 250V @ 100mA European Glass Fuse (5x20mm) - (AD8837)
Regular price $0.62 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
FM-0.2A 250V @ 200mA European Glass Fuse (5x20mm) - (AD47852)
Regular price $0.35 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
FN-0.25A 250V @ 250mA American Glass Fuse (6x32mm) - (AD904)
Regular price $0.35 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
FM-0.25A 250V @ 250mA European Glass Fuse (5x20mm) - (AD2793)
Regular price $0.35 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
FM-0.315A 250V @ 315mA European Glass Fuse (5x20mm) - (AD21013)
Regular price $0.53 USDRegular priceUnit price / per

![GC-0930 Automotive ATC Fuse Kit [10 PCS] - (AD57299)](http://www.microjpm.store/cdn/shop/files/AD57299uJPM.jpg?v=1749685061&width=533)
![65900 Automotive Mini Fuse Kit [10 PCS] - (AD30287)](http://www.microjpm.store/cdn/shop/files/AD30287uJPM-3_1.jpg?v=1749685365&width=533)
![ES1373A-KIT Automotive Micro Fuse Kit [10 PCS] - (AD30036)](http://www.microjpm.store/cdn/shop/files/AD30036uJPM-6.jpg?v=1749686032&width=533)